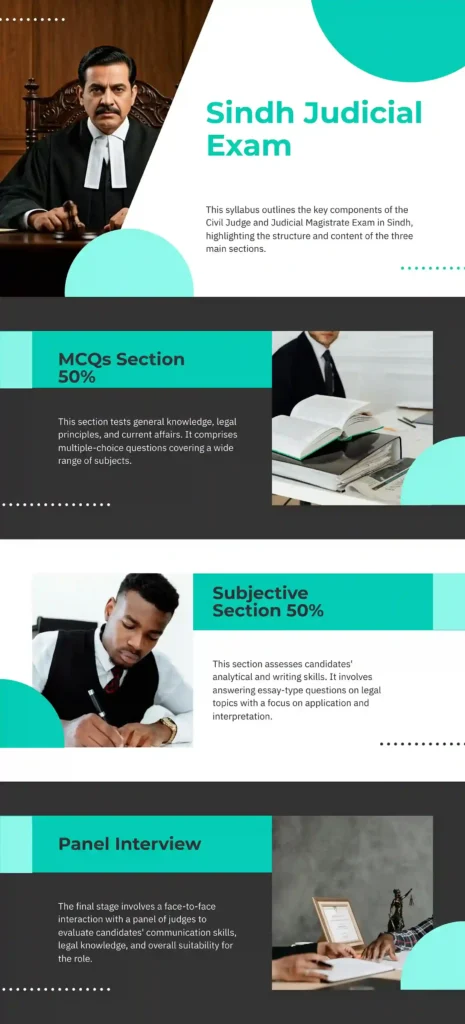
The Civil Judge and Judicial Magistrate Exam in Sindh is one of the most prestigious judicial exams in Pakistan. This exam is conducted to recruit civil judges and magistrates who play a vital role in the judicial system. If you are preparing for this exam, understanding the complete syllabus and exam pattern is essential for success.
In this blog, we will provide a detailed syllabus, exam pattern, study strategies, valuable resources, and frequently asked questions (FAQs) to help aspiring candidates.
The exam is divided into three main sections:
Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) Section
Subjective Section
Panel Interview
The passing criteria for each section are as follows:
MCQs: Minimum 50% marks required to qualify.
Subjective Section: Minimum 50% marks required.
Panel Interview: Final assessment by a panel of judges.
Books promulgation year
Important sections, orders, and articles
Limitations (Appeal, review, revision – Criminal, Civil, and Family Law)
Constitution of Pakistan 1973
Qanoon-e-Shahadat (Law of Evidence)
CrPC (Criminal Procedure Code)
CPC (Civil Procedure Code)
Contract Act
Family Laws
Specific Relief Act
Special Laws (Child Marriage Act, Temporary Resident Act, etc.)
Current affairs (Last 6 months English newspapers)
World Cups and Pakistan-related sports events
Historical dates and years
COVID-19 and pandemic laws
United Nations (UN), ICJ, and international laws
Presidents of the US
China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC)
Famous geographical locations and names
Recent bills and ordinances
Science knowledge (Solar System, Nobel Prize, etc.)
Nature (Oceans, peaks, rivers, mountains, etc.)
Revenue terms
Constitution of Pakistan (National Assembly seats, etc.)
Islamic history and religion
Pakistan Studies
Reading comprehension
Idioms
Synonyms and antonyms
Choosing the best meaning
IELTS-related questions
Complete the sentence exercises
Prepositions
Word meanings
Word relationships

Legal Drafting: Petition writing, case laws analysis, legal arguments
Essay Writing: Topics on law, constitution, and current affairs
Precise Writing: Summarization and critical analysis of legal texts
Translation: English to Urdu and vice versa
Candidates who clear the MCQs and subjective sections are invited for a panel interview.
The panel consists of senior judges and legal experts.
Focus areas include:
Legal knowledge
Ethics and judicial conduct
Logical reasoning and problem-solving skills
General awareness and confidence
Here’s a structured study plan to help you ace the exam:
2-3 Hours: MCQs Practice (Law, General Knowledge, and English)
3-4 Hours: Subjective Preparation (Essay, Legal Drafting, and Translation)
1 Hour: Newspaper reading for current affairs and legal updates
Mock Tests: Weekly full-length tests to assess progress
Books:
“Pakistan Penal Code” by M. Mahmood
“Constitution of Pakistan 1973” by Mansoor Book House
“Qanoon-e-Shahadat” by Shaukat Mehmood
“General Knowledge 2025 Edition” by ilmi Publishers
Online Platforms:
Judiciary Preparation YouTube Channels
Legal Study Groups on Facebook and Telegram
Past Papers from High Court Websites
Becoming a Civil Judge or Judicial Magistrate is a prestigious career path that requires dedication, knowledge, and strategic preparation. By following this comprehensive guide, you can effectively manage your studies and maximize your chances of success.
For more guidance, visit MAH Legal, a top law firm in Karachi, recognized for providing expert legal services and guidance to aspiring lawyers and judicial candidates.
© 2025 MAH&Co. All Rights Reserved | Disclaimer